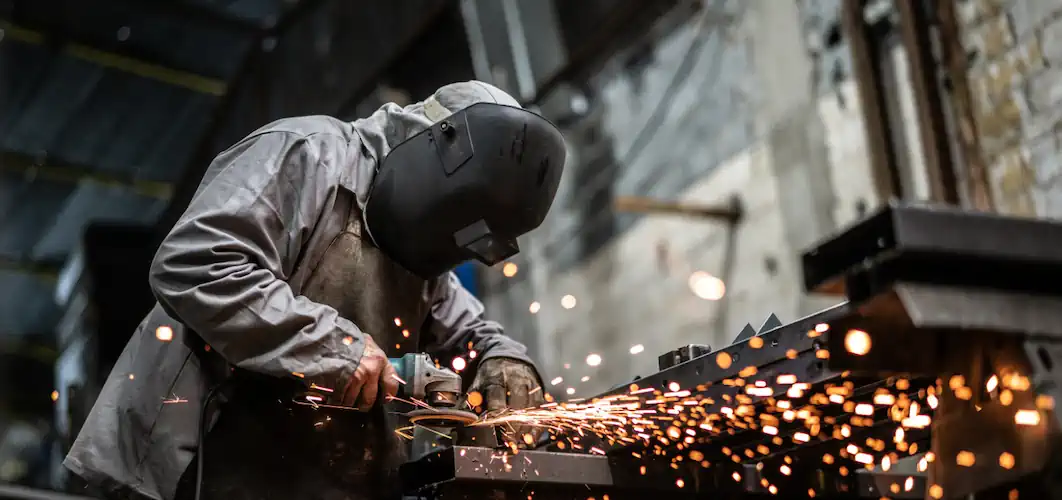
Metal Casting PPE 101: Protecting Workers

Working with metal casting presents a unique set of potential hazards, ranging from burns and lacerations to exposure to hazardous materials. To protect metal casting workers from being exposed to these dangers in the workplace, employers need to make use of protective equipment (PPE).
In the following article, the necessary PPE to protect metal casting workers will be explained in detail, along safe working practices, training, and a real-life example.
Table of Contents
1. Aluminized Leggings
2. Apron
3. Earplugs or Earmuffs
4. Face Shields
5. Foundry Jackets
6. Gloves
7. High-temperature Sleeves
8. Respirators
9. Safety Footwear
10. Safety Glasses/Face Shields
11. Safety Footwear
12. Heat-resistant Clothing
Metal Casting PPE
1. Aluminized Leggings
Aluminized leggings are made of a heat-resistant fabric that covers the legs from the waist to the ankle. They are usually worn over clothing to protect the wearer from high temperatures and molten metal splash.
2. Apron
An apron is a piece of clothing that is worn over the front of the body to protect clothing from getting dirty or damaged. Aprons are often made of materials such as leather, denim, or canvas.
In the metal casting industry, aprons are often made of heat-resistant materials such as aluminized glass-fibers or aramids. They help protect the wearer from high temperatures and molten metal splash.
3. Earplugs or Earmuffs
In the metal casting industry, earplugs or earmuffs are often worn to protect against noise generated by machineries such as furnaces, foundry ladles, and air compressors. They can also help protect against hearing loss caused by exposure to high noise levels over time.
4. Face Shields
A face shield is a clear plastic screen that is worn over the face to protect it from flying debris, molten metal splash, and other hazards. Face shields are often worn with other items of PPE such as safety glasses or respirators. In the metal casting industry, face shields help protect workers from exposure to high temperatures and dangerous chemicals.
5. Foundry Jackets
A foundry jacket is a heavy-duty coat that is worn to protect workers from high temperatures and molten metal splash. Foundry jackets are often made of materials such as aluminized viscoses or aramids. In the metal casting industry, they help protect workers from being burned by hot metals or coming into contact with dangerous chemicals.
6. Gloves
Gloves are worn to protect the hands from hot metals and other hazards. They are usually made of fire-resistant materials such as glass fibers or aramids.
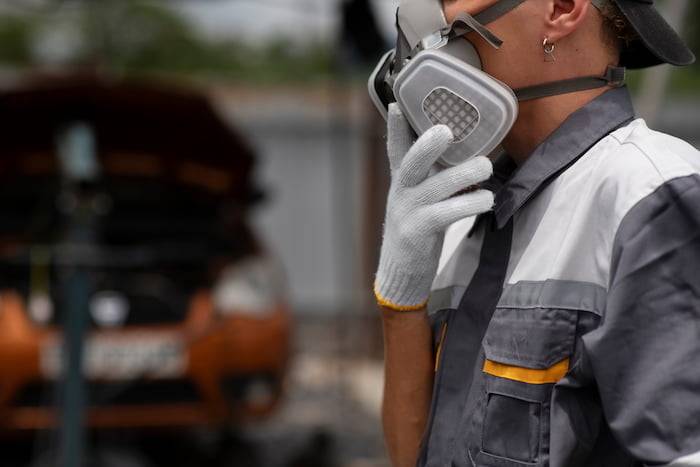

7. High-temperature Sleeves
High-temperature sleeves are made of a heat-resistant material and are worn over the arms to protect them from heat and sparks.
8. Respirators
A respirator is a device that covers the nose and mouth to filter out harmful fumes and dust particles. Respirators come in different types, including half-mask respirators, full-face respirators, and powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs).
9. Safety Footwear
Safety footwear is specially designed to protect the feet from hazards such as falling objects, electrical shocks, and slippery surfaces. Safety footwear includes shoes, boots, and sandals, which are often made from durable materials like steel.
10. Safety Glasses/Face Shields
Safety glasses or a face shield should be worn to protect the eyes from flying debris, dust particles, and chemicals. Face shields provide more protection than safety glasses alone. However, they can fog up easily, so it is important to choose one that has an anti-fog coating.
11. Safety Footwear
Safety footwear is specially designed to protect the feet from hazards such as falling objects, electrical shocks, and slippery surfaces. Safety footwear includes shoes, boots, and sandals, which are often made from durable materials like steel.
12. Heat-resistant Clothing
Heat-resistant clothing is made of a special fabric that does not burn easily. It is often used in foundries and other environments where there is exposure to high temperatures or flames. Heat-resistant clothing includes gloves, aprons, jackets, trousers, and boots.
Safe Work Practices
Working in any type of industrial environment is dangerous. The metal casting industry is no exception. However, with the right safety practices, you can protect your employees and your business from unnecessary risk.
Here are a few safety practices to follow on-site to ensure employee safety and health while minimizing your business’s liability exposure at the same time.
- Proper Machine Guarding
Machine guarding involves the installation of physical barriers to prevent workers from coming into
contact with
moving parts on machinery used in the metal casting process. Properly installed machine guards can
also help
reduce noise levels and keep dust particles at bay.
- Fire Prevention
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures
The lockout/tagout procedure is an important part of any safety program in the metal casting industry. This procedure involves locking out or tagging out all energy sources before performing maintenance or repairs on equipment.
By doing this, it ensures that no one will accidentally come into contact with live electricity while repairs are being performed. This procedure should always be followed whenever maintenance or repairs are needed on any type of equipment used in the metal casting process.
- Engineering Controls
Engineering controls involve designing your workspace in such a way that it minimizes exposure for workers and keeps them safe from hazards associated with the creation of highly engineered castings and hot metals.
This includes installing proper ventilation systems to dissipate heat, using special ovens or furnaces that are designed to reduce heat exposure, and installing proper shielding on machines or tools with higher chances of exposure to scathing temperatures during operation.
Another aspect of engineering controls is providing workers with proper training regarding how to handle hazardous materials safely as well as how to use the necessary protective equipment correctly while performing their tasks.
The most important safety measure is always following instructions provided by your supervisor or company policies when handling any type of hot metal – no matter what type of task you are performing.
- Ergonomic Design Of Workstations
Ergonomics plays an important role in the design of workstations used for metal casting processes. Ergonomically designed workstations provide comfort for operators while reducing fatigue and strain on their bodies which can lead to injuries or illnesses over time if not addressed properly.
Some ergonomic elements that should be considered when designing a workstation include adequate workspace, adjustable chairs or stools, adjustable heights for tools and instruments, and adequate lighting for visibility purposes.
It’s important to consult with a qualified professional when designing and installing machine guards as some machines have certain requirements that must be met to ensure their safe operation.
All fire prevention measures must be followed when dealing with molten metals like aluminum and zinc because these materials are highly flammable. Every workspace should have marked fire exits, fire extinguishers located throughout the area, and emergency response plans in place if a fire does occur. Additionally, it’s important to keep combustible materials away from any open flames or heated metals.

Training and Education
Working in metal casting is a difficult job, but one that can be made easier with the proper training and education. For professionals in this field, it is essential to know about metal casting processes, risk assessment, and proper PPE use.
This knowledge can be acquired through specialized training courses and certifications. Let’s take a closer look at the benefits of training and education for metal casting professionals.
- Benefits Of Training
Training is key to developing a knowledgeable, competent workforce that understands the safety requirements associated with metal casting operations. It also allows workers to become more familiar with the process and develop better problem-solving skills to handle any challenges that may arise. Furthermore, employers are likely to have access to lower insurance premiums when their employees are properly trained following industry standards.Training courses provide an in-depth overview of topics such as risk assessment, PPE use, process control techniques, quality control procedures, troubleshooting methods, etc. This type of hands-on learning allows workers to gain a deeper understanding of how each element works together to ensure safe operations throughout the entire process. Additionally, many courses offer certificates upon completion so that workers can demonstrate their competence on the job site.
- Benefits Of Education
Education plays an important role in helping employees understand the fundamentals behind metal casting processes so they can make informed decisions about how best to approach each task or operation. Educational programs often teach workers how to identify potential hazards associated with different aspects of their work and then apply appropriate solutions or countermeasures accordingly.They also help technicians become proficient in various metallurgy techniques used in the industry today such as heat treating metals or analyzing grain structure using microscopy analysis tools.
Case Studies
There have been numerous cases in the past involving disabling and non-disabling accidents in the metal casting industry as well as foundries. The constantly changing specifications from product to product make it impossible to standardize operations and workers are required to be fewer specialists and be more versatile with various types of foundry operations.
While molding and demolding are average on the scale of possible metal casting accidents, melting metal, cleaning, chipping, and finishing are the most hazardous elements of the process that pose a higher range of accidents among metal casting workers.
Practically, almost all workers are subject to certain hazards despite their operation on the work floor. Every worker faces the risk of getting their toes or fingers crushed while moving heavy materials with more chances of sprains. When in the vicinity of pouring molten metal into molds, the possibility of getting burnt by metal splashes is common.
Piled materials and the shifting of materials overhead via cranes and lifts are other possible dangers lurking around the corners.
- Defective Equipment
In one injury case, defective casting equipment was at the core of the issue resulting in the death of one worker and causing second and third-degree burns to three others. Four workers were involved in the metal pouring process when the casting die filled with the molten metal ruptured, throwing the liquid metal on the workers. The equipment lacked proper safety guards and was poorly designed concerning other safety features. - Occupational Hazard
In a more unsettling incident, the monitoring equipment of a facility malfunctioned, after which a breakdown team was dispatched to the spot to undertake repairs. However, the efforts were uncoordinated with the operational management and resulted in more serious predicaments.While hazardous gasses started escaping the facility, a team of firefighters was sent in to rectify the situation without any clue of the concentration of the gasses. This series of errors, both manual and mechanical, resulted in the death of three people and serious gas poisoning of various degrees for 22 other people involved.
In studies targeting such metal casting accidents, statistics reveal that simply having immediate medical attention on site drastically reduces the overall rate of injuries and serious health issues. And while in most cases the workers are blamed for such mishaps, oftentimes, defective equipment and errors like unplanned coordination, communication, and lack of situational awareness results in equally life-threatening accidents.
Final Thoughts On The Risks Of Metal Casting
The metallurgy and foundry industries are involved in the production of essential raw materials for a variety of products. Understanding the metal casting process is essential to help improve risk assessment and hazard identification. Creating an action plan to address the identified risks and using the appropriate PPE when dealing with molten metals can help prevent injuries and deaths.
Safe work practices should always be followed on-site such as proper machine guarding, fire prevention measures, lockout/tagout procedures, and engineering controls. Training and education are necessary for professionals in this field to understand safety requirements, gain problem solving skills, become familiar with processes and develop proficiency in metallurgy techniques.
FAQ Section
- What PPE should be worn with metal casting?
- What are some safety hazards in metal casting?
- What are safe work practices in metal casting?
- What are the benefits of training and education for metal casting professionals?
When metal casting it is necessary to wear protective equipment like gloves, long-sleeved shirt, safety eyewear, protective face shields, and more. Depending on how big the risk is, the protective gear needs to be greater.
It is important to follow safety practices like proper machine guarding, fire prevention, lockout and tagout procedures. Where employees will reduce the risk of getting electrocuted, reduce noise level, and have marked exits.
Common safe work hazards in metal casting include burns, falls, exposure to hazard materials, mechanical hazards and even chemical exposure.
The benefits of training and education for metal casting workers include improved safety awareness, enhanced skills in metal casting processes, and a better understanding of handling hazardous materials.